spring ioc源码解析
网上资料很多也很杂,这玩意我在公司开过session专门讲过,也算是比较了解,这里不啰嗦,直接用springboot的源码结合网上的资料总结下。
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(xxx.class, args);
}
构造器
略过一些,直接先点击构造方法
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// resourceLoader 属性,资源加载器。
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 被@configuration标记过的类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 推断当前环境是哪种Web环境,详见下面
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
// 注意下面这两个方法,他们都调用的事getSpringFactoriesInstances
// 所以这里拿到的东西都是从SpringFactories里加载的
// 同时,这里SpringFactoriesLoader会把SpringFactories里的内容加载到其内部的cache里
// 方便以后获取
// 创建ApplicationContextInitializer实例,详见下面
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 初始化 listeners 属性
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
// 加载REACTIVE容器还是SERVLET容器或者是default容器
private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
/**
* 获得指定类型的数组
* @param type
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 加载在 `META-INF/spring.factories` 里的类名的数组
// 在 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中,会以 KEY-VALUE 的格式,配置每个类对应的实现类们, 这里只拿keys
// 这都是一些spring boot启动需要加载的组建
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 创建对象们
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
// 进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
关于ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener,上两张图:
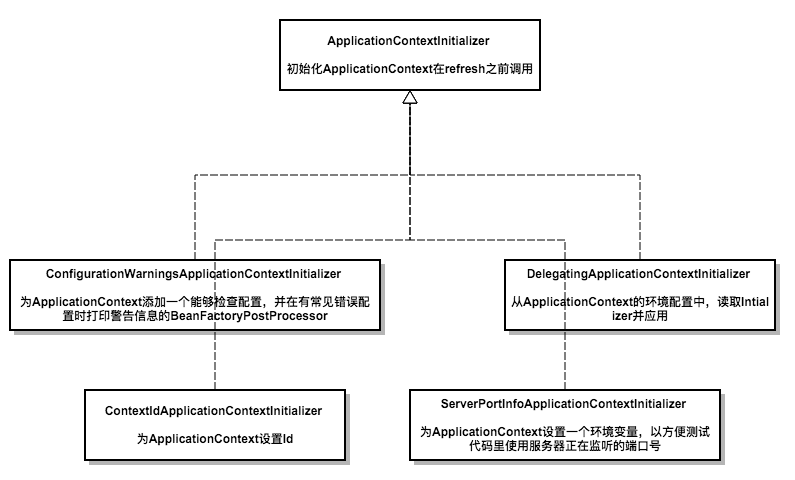
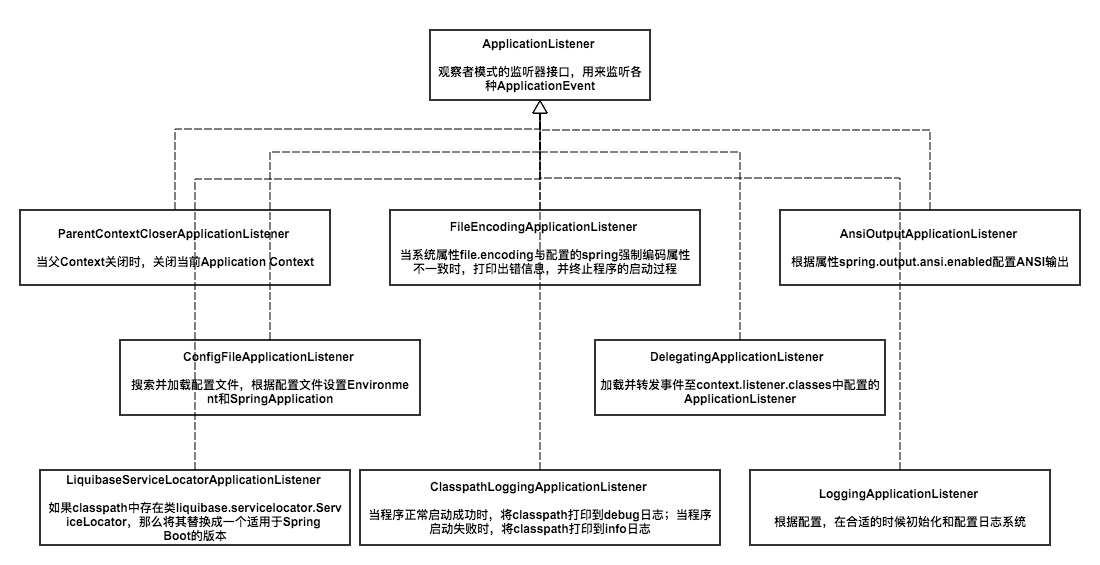
这个构造器最主要就是准备了ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener,为接下来的run做准备
说一下listener,因为用的比ApplicationContext少。
ApplicationEvent以及Listener是Spring为我们提供的一个事件监听、订阅的实现,内部实现原理是观察者设计模式,设计初衷也是为了系统业务逻辑之间的解耦,提高可扩展性以及可维护性。事件发布者并不需要考虑谁去监听,监听具体的实现内容是什么,发布者的工作只是为了发布事件而已。
好处是可以实现异步的事件发布和监听。
创建事件 ApplicationEvent
@Getter
public class PushOrderEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String orderNo;
private Long userId;
public PushOrderEvent(Object source, String orderNo,Long userId) {
super(source);
this.orderNo = orderNo;
this.userId = userId;
}
}
创建监听器 ApplicationListener
实现接口方式
@Slf4j
@Component
public class PushOrderListener implements ApplicationListener<PushOrderEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(PushOrderEvent event) {
log.info("{}用户下了一个订单{}", event.getUserId(), event.getOrderNo());
}
}
注解方式
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AnnotationPushOrderListener {
@EventListener
public void handler(PushOrderEvent event) {
log.info("{}用户下了一个订单{}", event.getUserId(), event.getOrderNo());
}
}
发布事件
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("order")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
@PostMapping("push")
public ResponseEntity pushOrder() {
String orderNo = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 发布事件
publisher.publishEvent(new PushOrderEvent(this, orderNo, 666666L));
return ResponseEntity.ok(orderNo);
}
}
run方法
先说一下需要了解的一些概念,便于后文理解
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 接口定义了一个你可以自己实现的回调方法,来实现你自己的实例化逻辑、依赖解决逻辑等,如果你想要在Spring完成对象实例化、配置、初始化之后实现自己的业务逻辑,你可以补充实现一个或多个BeanPostProcessor的实现。
BeanPostProcessor有两个方法:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean bean的实例
* @param beanName bean的name
* @return 返回处理过后的bean,可以是最初的Bean或者是包装后的Bean;
* 如果返回null,后续的BeanPostProcessor不会被执行
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean bean的实例
* @param beanName bean的name
* @return 返回处理过后的bean,可以是最初的Bean或者是包装后的Bean;
* 如果返回null,后续的BeanPostProcessor不会被执行
* {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
我们可以看到注释postProcessBeforeInitialization方法是在所有的bean的InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法之前执行而postProcessAfterInitialization方法则是在所有的bean的InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法之后执行的。
BeanFactoryProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的定义和BeanPostProcessor相似,有一个最主要的不同是:BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以对bean的配置信息进行操作;更确切的说Spring IOC容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor读取配置信息并且能够在容器实例化任何其他bean(所有的实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类)之前改变配置信息
*/
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
我们可以看到注释中写到的:postProcessBeanFactory可以在BeanFactory完成实例化后修改容器内部的BeanFactory。这时候所有的bean都被加载,但是没有bean被初始化。这就允许BeanFactoryPOSTProcessor重写或者添加配置,甚至可以提前初始化bean。
开始正题run():
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
// 可变个数参数args即是我们整个应用程序的入口main方法的参数,在我们的例子中,参数个数为零。
// SpringApplication对象的run方法创建并刷新ApplicationContext
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// StopWatch是来自org.springframework.util的工具类,可以用来方便的记录程序的运行时间。
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置headless模式, 没啥用,不关心
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 这个RunListener是在SpringApplication对象的run方法执行到不同的阶段时,发布相应的event给SpringApplication对象的成员变量listeners中记录的事件监听器。
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
// 正常没有args
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 准备environment,详见下文
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
// 在environment中将需要ignore的bean设为true
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 通过反射去初始化ApplicationContext,并实例化了其三个属性:
// 1、reader(AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader)
// 2、scanner(ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner)
// 3、beanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory)
context = createApplicationContext();
// 把ExceptionReporter加载一遍
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 准备Context,详见下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// 最重要的部分,详见下文
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
// 准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment 创建和配置环境
// 获取或创建环境
// Environment接口是Spring对当前程序运行期间的环境的封装。主要提供了两大功能:profile和property(父接口PropertyResolver提供)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境:配置PropertySources和activeProfiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// listeners环境准备(就是广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件)
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 将环境绑定到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 如果是非web环境,将环境转换成StandardEnvironment
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
// 配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
// 准备Context
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置上下文的environment
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 应用上下文后处理,一般不会处理啥
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 在context refresh之前,对其应用ApplicationContextInitializer,详见下文
applyInitializers(context);
// 一个空的实现
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
// 打印启动日志和启动应用的Profile
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
// 向beanFactory注册一个单例bean:命令行参数bean(正常实现没有)
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
// 向beanFactory注册一个单例bean:banner bean
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// Load the sources
// 获取全部资源,其实就一个:SpringApplication的primarySources(主类)属性
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 实例化了BeanDefinitionLoader,并调用AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#doRegisterBean,并将主类的BeanDefinition注册到context中的beanFactory的BeanDefinitionMap中
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 向上下文中添加ApplicationListener,并广播ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
/**
* Apply any {@link ApplicationContextInitializer}s to the context before it is
* refreshed.
* @param context the configured ApplicationContext (not refreshed yet)
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
*/
// 一共6个initializer,他们的initialize方法都被调用
// 1、DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer:如果配置了context.initializer.classes,获取其值(逗号分隔的initializer列表字符串),转换成class列表
// 根据classes列表进行实例化获取initializer实例列表,再对每个initializer实例调用initialize方法。
// 2、ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer:设置application id:从environment中获取spring.application.name配置项的值,并把设置成application id
// 若没有配置spring.application.name,则取默认值application;将application id封装成ContextId对象,注册到beanFactory中。
// 3、ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer:向上下文注册了一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor实例
// 4、ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer:向上下文注册了一个ApplicationListener:ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer对象自己
// 5、SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer:向context注册了一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor实例。
// 6、ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener:向上下文注册了一个ApplicationListener:ConditionEvaluationReportListener实例;
// 从beanFactory中获取名为autoConfigurationReport的bean赋值给自己的属性report
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
// 解析当前initializer实现的ApplicationContextInitializer的泛型参数
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(
initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
// 断言context是否是requiredType的实例
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
// 向context应用初始化器
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
把refreshContext(context)拿出来单独说,他实际上是调用了AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 两步:
// 1、initPropertySources() 默认空实现
// 2、getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 默认没有RequiredProperties
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 给BeanFactory设了一个ID叫application
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 详见下文
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 默认没有实现,如果是web项目的话,会注册web-specific scopes ("request", "session", "globalSession")和web-specific environment beans ("contextParameters", "contextAttributes")
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 处理BeanFactoryPostProcessors,会注册bean,实例化bean,并调用其方法
// 调用的是invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,详见下文
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 处理beanpostprocessor,会注册bean,实例化bean,以供bean创建的时候使用,详见下文
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 针对于国际化问题的MessageSource,这里略过,不是很重要
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件监听多路广播器
// 没有的话就注册一个simpleApplicationEventMulticaster就是用来发布事件用的。
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 空方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有剩余的非懒加载单例 bean。
// 除了一些内部的 bean、实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 bean、实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口的 bean,
// 其他的非懒加载单例 bean 都会在这个方法中被实例化,并且 BeanPostProcessor 的触发也是在这个方法中。
// 详见下文
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 详见下文
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 默认是appclassloader
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 注册语言解析器,就可以对SPEL进行解析了
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
// 为beanFactory增加了一个默认的propertyEditor,这个主要是对bean的属性等设置管理的一个工具
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加BeanPostProcessor--ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
// ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:让Application contexts自动注册他潜在依赖的bean factory,默认不会启用,后面给ignore了
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 设置了几个忽略自动装配的接口
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 设置了几个自动装配的特殊规则
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
// 增加对AspectJ的支持
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 添加默认的系统环境bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
// 1.判断beanFactory是否为BeanDefinitionRegistry,beanFactory为DefaultListableBeanFactory,
// 而DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,因此这边为true
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// 用于存放普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// 用于存放BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// 2.首先处理入参中的beanFactoryPostProcessors
// 遍历所有的beanFactoryPostProcessors, 将BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor区分开
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
// 2.1 如果是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 2.1.1 直接执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法(一般是在BeanFactory里注册或修改BeanDefinition)
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
// 2.1.2 添加到registryProcessors(用于最后执行postProcessBeanFactory方法)
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
} else {
// 2.2 否则,只是普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 2.2.1 添加到regularPostProcessors(用于最后执行postProcessBeanFactory方法)
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
// 用于保存本次要执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 3.再处理bean factory里的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
// 调用所有实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类
// 3.1 找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的Bean的beanName
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 3.2 遍历postProcessorNames
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 3.3 校验是否实现了PriorityOrdered接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 3.4 获取ppName对应的bean实例, 添加到currentRegistryProcessors中,
// beanFactory.getBean: 这边getBean方法会触发创建ppName对应的bean对象, 目前暂不深入解析
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 3.5 将要被执行的加入processedBeans,避免后续重复执行
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 3.6 进行排序(根据是否实现PriorityOrdered、Ordered接口和order值来排序)
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 3.7 添加到registryProcessors(用于最后执行postProcessBeanFactory方法)
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 3.8 遍历currentRegistryProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
// **这里划重点** 因为这里会执行spring中最重要的一个beanfactory后置加载器:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
// 做什么的我在后文说
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 3.9 执行完毕后, 清空currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 4.调用所有实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类(过程跟上面的步骤3基本一样)
// 4.1 找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类, 这边重复查找是因为执行完上面的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
// 可能会新增了其他的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, 因此需要重新查找
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 校验是否实现了Ordered接口,并且还未执行过
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 4.2 遍历currentRegistryProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
// 5.最后, 调用所有剩下的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
// 5.1 找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 5.2 跳过已经执行过的
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
// 5.3 如果有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor被执行, 则有可能会产生新的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
// 因此这边将reiterate赋值为true, 代表需要再循环查找一次
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 5.4 遍历currentRegistryProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// 6.调用所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 7.最后, 调用入参beanFactoryPostProcessors中的普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 到这里 , 入参beanFactoryPostProcessors和容器中的所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor已经全部处理完毕,
// 下面开始处理容器中的所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// 8.找出所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
String[] postProcessorNames =v
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 用于存放实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// 用于存放实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的beanName
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 用于存放普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor的beanName
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 8.1 遍历postProcessorNames, 将BeanFactoryPostProcessor按实现PriorityOrdered、实现Ordered接口、普通三种区分开
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 8.2 跳过已经执行过的
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 8.3 添加实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
// 8.4 添加实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的beanName
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
} else {
// 8.5 添加剩下的普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor的beanName
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 9.调用所有实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 9.1 对priorityOrderedPostProcessors排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 9.2 遍历priorityOrderedPostProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 10.调用所有实现Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 10.1 获取postProcessorName对应的bean实例, 添加到orderedPostProcessors, 准备执行
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 10.2 对orderedPostProcessors排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 10.3 遍历orderedPostProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
// 11.调用所有剩下的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 11.1 获取postProcessorName对应的bean实例, 添加到nonOrderedPostProcessors, 准备执行
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 11.2 遍历nonOrderedPostProcessors, 执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
// 12.清除元数据缓存(mergedBeanDefinitions、allBeanNamesByType、singletonBeanNamesByType),
// 因为后处理器可能已经修改了原始元数据,例如, 替换值中的占位符...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
这里要单独把ConfigurationClassPostProcessor拿出来说一下,这是一个BeanFactory的后置处理器,因此它的主要功能是参与BeanFactory的建造,在这个类中,会解析加了@Configuration的配置类,还会解析@ComponentScan、@ComponentScans注解扫描的包,以及解析@Import等注解。
这里我们直接看它所调用的主要方法
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取现有的BeanDefinitionName,此时应该只有主类,和一些AnnotationProcessor,listener
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
// log 日志
}
// checkConfigurationClassCandidate()会判断一个是否是一个配置类,并为BeanDefinition设置属性为lite或者full。
// 在这儿为BeanDefinition设置lite和full属性值是为了后面在使用
// 如果加了@Configuration,那么对应的BeanDefinition为full;
// 如果加了@Bean,@Component,@ComponentScan,@Import,@ImportResource这些注解,则为lite。
// lite和full均表示这个BeanDefinition对应的类是一个配置类
// 尽管如此,因为这里是对上文的candidate进行一个过滤
// 所以一般这里过滤后只剩一个主类
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// ... 省略部分代码
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
// beanName的生成器,因为后面会扫描出所有加入到spring容器中class,然后把这些class
// 解析成BeanDefinition类,此时需要利用BeanNameGenerator为这些BeanDefinition生成beanName
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
// ... 省略部分代码
// 解析所有加了@Configuration注解的类
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
// 解析配置类,在此处会解析配置类上的注解(ComponentScan扫描出的类,@Import注册的类,以及@Bean方法定义的类)
// 注意:这一步只会将加了@Configuration注解以及通过@ComponentScan注解扫描的类才会加入到BeanDefinitionMap中
// 通过其他注解(例如@Import、@Bean)的方式,在parse()方法这一步并不会将其解析为BeanDefinition放入到BeanDefinitionMap中,而是先解析成ConfigurationClass类
// 真正放入到map中是在下面的this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions()方法中实现的
// 而且这里不会为bean解析依赖,即BeanDefinition的dependsOn属性是空的
// 详见下文
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
// 将上一步parser解析出的ConfigurationClass类加载成BeanDefinition
// 实际上经过上一步的parse()后,解析出来的bean已经放入到BeanDefinition中了,但是由于这些bean可能会引入新的bean,例如实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar或者ImportSelector接口的bean,或者bean中存在被@Bean注解的方法
// 因此需要执行一次loadBeanDefinition(),这样就会执行ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar或者ImportSelector接口的方法或者@Bean注释的方法
// 实际上是执行loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass方法,见下文
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
// 这里判断registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length的目的是为了知道reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses)这一步有没有向BeanDefinitionMap中添加新的BeanDefinition
// 实际上就是看配置类(例如AppConfig类会向BeanDefinitionMap中添加bean)
// 如果有,registry.getBeanDefinitionCount()就会大于candidateNames.length
// 这样就需要再次遍历新加入的BeanDefinition,并判断这些bean是否已经被解析过了,如果未解析,需要重新进行解析
// 这里的AppConfig类向容器中添加的bean,实际上在parser.parse()这一步已经全部被解析了
// 所以为什么还需要做这个判断,在processConfigBeanDefinitions的过程中, 有可能会动态添加beanDefinition到beanDefinitionMap, 这样就会导致两次的数量不一致
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
// 如果有未解析的类,则将其添加到candidates中,这样candidates不为空,就会进入到下一次的while的循环中
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new LinkedList<>();
// 根据BeanDefinition类型的不同,调用parse()不同的重载方法
// 实际上最终都是调用doProcessConfigurationClass()方法
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
// 处理延迟importSelector
// 也是真正处理spring的AutoConfiguration的方法
// 详见下文
processDeferredImportSelectors();
}
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
// 1、首先处理内部类,处理内部类时,最终还是调用doProcessConfigurationClass()方法
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass);
// 2、处理属性资源文件,加了@PropertySource注解
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
}
// 3、处理@ComponentScan或者@ComponentScans注解
// 3.1 先找出类上的@ComponentScan和@ComponentScans注解的所有属性(例如basePackages等属性值)
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// 3.2 解析@ComponentScan和@ComponentScans配置的扫描的包所包含的类
// 比如 basePackages = com.tiantang.study, 那么在这一步会扫描出这个包及子包下的class,然后将其解析成BeanDefinition
// (BeanDefinition可以理解为等价于BeanDefinitionHolder)
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 3.3 通过上一步扫描包com.tiantang.com下的类,有可能扫描出来的bean中可能也添加了ComponentScan或者ComponentScans注解.
//所以这里需要循环遍历一次,进行递归(parse),继续解析,直到解析出的类上没有ComponentScan和ComponentScans
// (这时3.1这一步解析出componentScans为空列表,不会进入到if语句,递归终止)
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
// 同样,这里会调用ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate()方法来判断类是否是一个配置类
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// 4.处理Import注解注册的bean,这一步只会将import注册的bean变为ConfigurationClass,不会变成BeanDefinition
// 而是在loadBeanDefinitions()方法中变成BeanDefinition,再放入到BeanDefinitionMap中
// 这里划重点
// @import那里用到过?看这里
// ···
// @Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector.class)
// public @interface EnableConfigurationProperties
// ···
// 也就是说,所有需要springboot自动装配的AutoConfiguration类,其实都是被@Import标注过的类
// !!但是,因为进到这个方法的时候,configCandidates是主类,除非在我们的主类的classpath下我们显示的声明了@import
// 否则这个方法只会把标注有@EnableAutoConfiguration的引入到deferredimport里供后面真正处理的时候使用(即主类)
// 当然后面调用processDeferredImportSelectors方法时,还是会重新进入这个方法
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
// 5.处理@ImportResource注解引入的配置文件
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// 处理加了@Bean注解的方法
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// ... 省略部分代码
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
// 来了,真正处理spring boot的AutoConfiguration的方法来了
private void processDeferredImportSelectors() {
// deferredImports就是我们刚刚处理过的主类
// Import注解的值是EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class
List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
if (deferredImports == null) {
return;
}
deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR);
Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Map<AnnotationMetadata, ConfigurationClass> configurationClasses = new HashMap<>();
for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : deferredImports) {
//以EnableAutoConfiguration注解为例,其Import注解的值为EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class,
//那么此处就是在调用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector的selectImports方法,返回了一个字符串数组
//这里就是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector$AutoConfigurationGroup
Class<? extends Group> group = deferredImport.getImportSelector().getImportGroup();
// 包装一个grouping,里面有beanfactory,bean classloader
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = groupings.computeIfAbsent(
(group != null ? group : deferredImport),
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group)));
// 把上面的deferredImports加进来
grouping.add(deferredImport);
configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getConfigurationClass());
}
for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : groupings.values()) {
// 这里划重点,这个getImports()得单独拿出来说
// 详见下文
grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = configurationClasses.get(entry.getMetadata());
try {
// 这个前文提到过了,用于把这些自动配置类加载到ConfigurationClass中
processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass),
asSourceClasses(entry.getImportClassName()), false);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
});
}
}
public Iterable<Group.Entry> getImports() {
for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : this.deferredImports) {
// getImports调用了AutoConfigurationImportSelector#process方法
this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getImportSelector());
}
return this.group.selectImports();
}
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata,
DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
// process再调用selectImports方法
String[] imports = deferredImportSelector.selectImports(annotationMetadata);
for (String importClassName : imports) {
this.entries.put(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 重点在这里了selectImports通过AnnotationMetadata去拿真正需要自动加载的类
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
// 删除重复的
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
// 删除exclude的
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
// filter一下那些有condition注解的
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
}
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 到这里,我们终于进来了,去SpringFactoriesLoader里去拿configurations
// 因为之前在最开始构造器阶段SpringFactoriesLoader就已经加载过了,这里就直接从cache里拿出来了
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {
// 省略部分代码 ...
// 如果一个bean是通过@Import(ImportSelector)的方式添加到容器中的,那么此时configClass.isImported()返回的是true
// 而且configClass的importedBy属性里面存储的就是需要注册为bean的类
if (configClass.isImported()) {
registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);
}
// 判断当前的bean中是否含有@Bean注解的方法,如果有,需要把这些方法产生的bean放入到BeanDefinitionMap当中
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources());
// 如果bean上存在@Import注解,且import的是一个实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,则执行ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的registerBeanDefinitions()方法
loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars());
}
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 1.找出所有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
// BeanPostProcessor的目标计数
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// 2.添加BeanPostProcessorChecker(主要用于记录信息)到beanFactory中
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 3.定义不同的变量用于区分: 实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor、实现Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor、普通BeanPostProcessor
// 3.1 priorityOrderedPostProcessors: 用于存放实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
// 3.2 internalPostProcessors: 用于存放Spring内部的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
// 3.3 orderedPostProcessorNames: 用于存放实现Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor的beanName
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 3.4 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames: 用于存放普通BeanPostProcessor的beanName
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 4.遍历postProcessorNames, 将BeanPostProcessors按3.1 - 3.4定义的变量区分开
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 4.1 如果ppName对应的Bean实例实现了PriorityOrdered接口, 则拿到ppName对应的Bean实例并添加到priorityOrderedPostProcessors
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
// 4.2 如果ppName对应的Bean实例也实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,
// 则将ppName对应的Bean实例添加到internalPostProcessors
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
// 4.3 如果ppName对应的Bean实例没有实现PriorityOrdered接口, 但是实现了Ordered接口, 则将ppName添加到orderedPostProcessorNames
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
// 4.4 否则, 将ppName添加到nonOrderedPostProcessorNames
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 5.首先, 注册实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessors
// 5.1 对priorityOrderedPostProcessors进行排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 5.2 注册priorityOrderedPostProcessors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 6.接下来, 注册实现Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessors
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 6.1 拿到ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例对象
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
// 6.2 将ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例对象添加到orderedPostProcessors, 准备执行注册
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
// 6.3 如果ppName对应的Bean实例也实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,
// 则将ppName对应的Bean实例添加到internalPostProcessors
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 6.4 对orderedPostProcessors进行排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 6.5 注册orderedPostProcessors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
// 7.注册所有常规的BeanPostProcessors(过程与6类似)
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
// 8.最后, 重新注册所有内部BeanPostProcessors(相当于内部的BeanPostProcessor会被移到处理器链的末尾)
// 8.1 对internalPostProcessors进行排序
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 8.2注册internalPostProcessors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
// 9.重新注册ApplicationListenerDetector(跟8类似,主要是为了移动到处理器链的末尾)
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
// 1.初始化此上下文的转换服务
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
// 2.如果beanFactory之前没有注册嵌入值解析器,则注册默认的嵌入值解析器:主要用于注解属性值的解析。
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
@Override
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
// 3.初始化LoadTimeWeaverAware Bean实例对象
// 尽早初始化LoadTimeWeaverAware bean,以便尽早注册它们的转换器。
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
// 禁止使用临时类加载器进行类型匹配
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
// 4.冻结所有bean定义,注册的bean定义不会被修改或进一步后处理,因为马上要创建 Bean 实例对象了
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 5.实例化所有剩余(非懒加载)单例对象
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 1.创建beanDefinitionNames的副本beanNames用于后续的遍历,以允许init等方法注册新的bean定义
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 2.遍历beanNames,触发所有非懒加载单例bean的初始化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 3.获取beanName对应的MergedBeanDefinition
// 实际就调用了getMergedBeanDefinition,详见下文
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 4.bd对应的Bean实例:不是抽象类 && 是单例 && 不是懒加载
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 5.判断beanName对应的bean是否为FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 5.1 通过beanName获取FactoryBean实例
// 通过getBean(&beanName)拿到的是FactoryBean本身;通过getBean(beanName)拿到的是FactoryBean创建的Bean实例
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
// 5.2 判断这个FactoryBean是否希望急切的初始化
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
} else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
// 5.3 如果希望急切的初始化,则通过beanName获取bean实例
getBean(beanName);
}
} else {
// 6.如果beanName对应的bean不是FactoryBean,只是普通Bean,通过beanName获取bean实例
// 调用dogetbean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 7.遍历beanNames,触发所有SmartInitializingSingleton的后初始化回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 7.1 拿到beanName对应的bean实例
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 7.2 判断singletonInstance是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
// 7.3 触发SmartInitializingSingleton实现类的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
} else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
一些需要知道的知识
MergedBeanDefinition
在之后的内容你可能会频繁的见到 “MergedBeanDefinition” 这个词,因此这边先稍微讲解一下,有助于你更好的理解。
MergedBeanDefinition:这个词其实不是一个官方词,但是很接近,该词主要是用来表示 “合并的 bean 定义”,因为每次都写 “合并的 bean 定义” 有点太绕口,因此我在之后的注释或解析中或统一使用 MergedBeanDefinition 来表示 “合并的 bean 定义”。
之所以称之为 “合并的”,是因为存在 “子定义” 和 “父定义” 的情况。对于一个 bean 定义来说,可能存在以下几种情况:
该 BeanDefinition 存在 “父定义”:首先使用 “父定义” 的参数构建一个 RootBeanDefinition,然后再使用该 BeanDefinition 的参数来进行覆盖。
该 BeanDefinition 不存在 “父定义”,并且该 BeanDefinition 的类型是 RootBeanDefinition:直接返回该 RootBeanDefinition 的一个克隆。
该 BeanDefinition 不存在 “父定义”,但是该 BeanDefinition 的类型不是 RootBeanDefinition:使用该 BeanDefinition 的参数构建一个 RootBeanDefinition。
之所以区分出2和3,是因为通常 BeanDefinition 在之前加载到 BeanFactory 中的时候,通常是被封装成 GenericBeanDefinition 或 ScannedGenericBeanDefinition,但是从这边之后 bean 的后续流程处理都是针对 RootBeanDefinition,因此在这边会统一将 BeanDefinition 转换成 RootBeanDefinition。
FactoryBean
一般情况下,Spring 通过反射机制利用 bean 的 class 属性指定实现类来实例化 bean。而 FactoryBean 是一种特殊的 bean,它是个工厂 bean,可以自己创建 bean 实例,如果一个类实现了 FactoryBean 接口,则该类可以自己定义创建实例对象的方法,只需要实现它的 getObject() 方法。
注:很多中间件都利用 FactoryBean 来进行扩展。
例如以下例子:
public class AppleFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Apple> {
@Override
public Apple getObject() throws Exception {
Apple apple = new Apple();
apple.setName("bigApple");
return apple;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Apple.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
为了区分 “FactoryBean” 和 “FactoryBean 创建的 bean 实例”,Spring 使用了 “&” 前缀。假设我们的 beanName 为 apple,则 getBean(“apple”) 获得的是 AppleFactoryBean 通过 getObject() 方法创建的 bean 实例;而 getBean(“&apple”) 获得的是 AppleFactoryBean 本身。
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(
String beanName, BeanDefinition bd, BeanDefinition containingBd)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 1.加锁再进行操作
synchronized (this.mergedBeanDefinitions) {
// 用于存储bd的MergedBeanDefinition,也就是该方法的结果
RootBeanDefinition mbd = null;
// Check with full lock now in order to enforce the same merged instance.
if (containingBd == null) {
// 2.检查beanName对应的MergedBeanDefinition是否存在于缓存中
mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
}
// 3.如果beanName对应的MergedBeanDefinition不存在于缓存中
if (mbd == null) {
if (bd.getParentName() == null) {
// 4.如果bd的parentName为空,代表bd没有父定义,无需与父定义进行合并操作,
// 也就是bd的MergedBeanDefinition就是bd本身(可能需要转成RootBeanDefinition)
// Use copy of given root bean definition.
if (bd instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
// 4.1 如果bd的类型为RootBeanDefinition,则bd的MergedBeanDefinition就是bd本身,则直接克隆一个副本
mbd = ((RootBeanDefinition) bd).cloneBeanDefinition();
} else {
// 4.2 否则,将bd作为参数,构建一个RootBeanDefinition。
// 正常使用下,BeanDefinition在被加载后是GenericBeanDefinition或ScannedGenericBeanDefinition
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(bd);
}
} else {
// 5.否则,bd存在父定义,需要与父定义合并
// Child bean definition: needs to be merged with parent.
BeanDefinition pbd;
try {
// 5.1 获取父定义的beanName
String parentBeanName = transformedBeanName(bd.getParentName());
// 5.2 如果父定义的beanName与该bean的beanName不同
if (!beanName.equals(parentBeanName)) {
// 5.3 获取父定义的MergedBeanDefinition(因为父定义也可能有父定义,也就是bd的爷爷定义...)
pbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
} else {
// 5.4 如果父定义的beanName与bd的beanName相同,则拿到父BeanFactory,
// 只有在存在父BeanFactory的情况下,才允许父定义beanName与自己相同,否则就是将自己设置为父定义
BeanFactory parent = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
// 5.5 如果父BeanFactory是ConfigurableBeanFactory,则通过父BeanFactory获取父定义的MergedBeanDefinition
pbd = ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) parent).getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
} else {
// 5.6 如果父BeanFactory不是ConfigurableBeanFactory,则抛异常
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(parentBeanName,
"Parent name '" + parentBeanName + "' is equal to bean name '" + beanName +
"': cannot be resolved without an AbstractBeanFactory parent");
}
}
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve parent bean definition '" + bd.getParentName() + "'", ex);
}
// Deep copy with overridden values.
// 5.7 使用父定义pbd构建一个新的RootBeanDefinition对象(深拷贝)
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(pbd);
// 5.8 使用bd覆盖父定义
mbd.overrideFrom(bd);
}
// Set default singleton scope, if not configured before.
// 6.如果没有配置scope,则设置成默认的singleton
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(mbd.getScope())) {
mbd.setScope(RootBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON);
}
// A bean contained in a non-singleton bean cannot be a singleton itself.
// Let's correct this on the fly here, since this might be the result of
// parent-child merging for the outer bean, in which case the original inner bean
// definition will not have inherited the merged outer bean's singleton status.
// 7.如果containingBd不为空 && containingBd不为singleton && mbd为singleton,则将mdb的scope设置为containingBd的scope
if (containingBd != null && !containingBd.isSingleton() && mbd.isSingleton()) {
mbd.setScope(containingBd.getScope());
}
// Cache the merged bean definition for the time being
// (it might still get re-merged later on in order to pick up metadata changes)
// 8.将beanName与mbd放到mergedBeanDefinitions缓存,以便之后可以直接使用
if (containingBd == null && isCacheBeanMetadata()) {
this.mergedBeanDefinitions.put(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// 9.返回MergedBeanDefinition
return mbd;
}
}
这边引入了一个 “父 BeanFactory” 的概念,稍微解释下。
父 BeanFactory
在 Spring 中可能存在多个 BeanFactory,多个 BeanFactory 可能存在 “父工厂” 与 “子工厂” 的关系。最常见的例子就是:Spring MVC 的 BeanFactory 和 Spring 的 BeanFactory,通常情况下,Spring 的 BeanFactory 是 “父工厂”,Spring MVC 的 BeanFactory 是 “子工厂”,在 Spring 中,子工厂可以使用父工厂的 BeanDefinition,因而,如果在当前 BeanFactory 中找不到,而又存在父工厂,则会去父工厂中查找。
public boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
// 1.拿到真正的beanName(去掉&前缀、解析别名)
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
// 2.尝试从缓存获取Bean实例对象
Object beanInstance = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (beanInstance != null) {
// 3.beanInstance存在,则直接判断类型是否为FactoryBean
return (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean);
} else if (containsSingleton(beanName)) {
// 4.如果beanInstance为null,并且beanName在单例对象缓存中,则代表beanName对应的单例对象为空对象,返回false
// null instance registered
return false;
}
// No singleton instance found -> check bean definition.
if (!containsBeanDefinition(beanName) && getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
// 5.如果缓存中不存在此beanName && 父beanFactory是ConfigurableBeanFactory,则调用父BeanFactory判断是否为FactoryBean
// No bean definition found in this factory -> delegate to parent.
return ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) getParentBeanFactory()).isFactoryBean(name);
}
// 6.通过MergedBeanDefinition来检查beanName对应的Bean是否为FactoryBean
return isFactoryBean(beanName, getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName));
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 如果这个 name 是 FactoryBean 的beanName (&+beanName),就删除& , 返回beanName ,传入的name也可以是别名,也需要做转换
// 注意 beanName 和 name 变量的区别,beanName是经过处理的,经过处理的beanName就直接对应singletonObjects中的key
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 根据beanName尝试从singletonObjects获取Bean
// 获取不到则再尝试从earlySingletonObjects,singletonFactories 从获取Bean
// 这段代码和解决循环依赖有关
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 第一次进入sharedInstance肯定为null
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
} else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 如果sharedInstance不为null,也就是非第一次进入
// 为什么要调用 getObjectForBeanInstance 方法,判断当前Bean是不是FactoryBean,如果是,那么要不要调用getObject方法
// 因为传入的name变量如果是(&+beanName),那么beanName变量就是(beanName),也就是说,程序在这里要返回FactoryBean
// 如果传入的name变量(beanName),那么beanName变量也是(beanName),但是,之前获取的sharedInstance可能是FactoryBean,需要通过sharedInstance来获取对应的Bean
// 如果传入的name变量(beanName),那么beanName变量也是(beanName),获取的sharedInstance就是对应的Bean的话,就直接返回Bean
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 判断是否循环依赖
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
// 获取父BeanFactory,一般情况下,父BeanFactory为null,如果存在父BeanFactory,就先去父级容器去查找
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
} else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
} else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
} else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
// 创建的Bean是否需要进行类型验证,一般情况下都不需要
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
// 标记 bean 已经被创建
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 获取其父类Bean定义,子类合并父类公共属性
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 获取当前Bean依赖的Bean的名称 ,@DependsOn
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 如果当前Bean依赖其他Bean,把被依赖Bean注册给当前Bean
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
// 先去创建所依赖的Bean
getBean(dep);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 创建单例Bean
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
// 创建prototype Bean,每次都会创建一个新的对象
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
// 回调beforePrototypeCreation方法,注册当前创建的原型对象
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 创建对象
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} finally {
// 回调 afterPrototypeCreation 方法,告诉容器该Bean的原型对象不再创建
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else {
// 如果既不是单例Bean,也不是prototype,则获取其Scope
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
// 创建对象
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
} catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
// 对创建的Bean进行类型检查
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
} catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
//getSingleton(beanName, true);源码
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// singletonObjects 就是Spring内部用来存放单例Bean的对象池, key为beanName,value为Bean
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 存放了当前正在创建的bean的BeanName
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// earlySingletonObjects 是早期单例Bean的缓存池, 此时Bean已经被创建(newInstance),但是还没有完成初始化
// key为beanName,value为Bean
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 是否允许早期依赖
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
//singletonFactories 单例工厂的缓存,key为beanName,value 为ObjectFactory
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
//获取早期Bean
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
//将早期Bean放到earlySingletonObjects中
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 确保此时实际解析了bean类
resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbd.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
//如果bean实现了实例化前处理器接口的,则需要在实例化之前调用这个方法
//bean的生命周期的中实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor会在这里调用实现的postProcessBeforeInstantiation
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbd);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbd, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
//BeanWrapper提供设置和获取属性值(单独或批量),获取属性描述符和查询属性以确定它们是可读还是可写的功能
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
//如果RootBeanDefinition是单例的,则移除未完成的FactoryBean实例的缓存
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建bean实例
//详见下文
//这里会在此方法里直接处理构造器的bean依赖,并实例化这些bean
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//获取BeanWrapper中封装的Object对象,其实就是bean对象的实例
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
//获取BeanWrapper中封装的bean的Class
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
//bean 的生命周期之一。如果实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor会在这里调用postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
//如果RootBeanDefinition是单例的,并且开启了自动尝试解析bean之间的循环引用,并且当前bean正在创建中,则说明这个bean需要被加入到缓存的单例bean集合中
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
/**
* addSingletonFactory会将beanName和ObjectFactory对象作为键值对保存到缓存的单例集合中
* singletonObjects: 单例对象的缓存 ConcurrentHashMap
* singletonFactories:单例工厂的缓存 HashMap
* earlySingletonObjects: 早期单例对象的缓存 HashMap
* registeredSingletons: 一组已经注册的单例,按注册顺序排序 LinkedHashSet
*/
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
// 处理循环依赖用,详见下文
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//进行属性填充
// 详见下文
// 这里会处理property(setter方法)的依赖
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
//初始化给定的bean实例,应用工厂回调以及init方法和bean后处理器
//详见下文
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
//如果单例bean已经缓存了,则直接获取
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
//如果不允许在循环引用的情况下使用注入原始bean实例(即使注入的bean最终被包装),并且依赖的bean列表中存在需要创建bean。这时候就说明存在循环依赖
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
//根据beanName获取所有依赖的bean的beanName
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
//删除存在循环依赖的bean
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
//将给定的bean添加到此一次性Bean列表中,这个列表中的bean在Spring关闭的时候会查询里面的bean,并调用实现的销毁方法(包含实现了DisposableBean接口的方法和自定义的destory方法),满足其中一个条件
// 1.实现了DisposableBean接口
//2.自定义了destroy方法
//3.实现了AutoCloseable接口
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
//获取RootBeanDefinition的Class属性
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
//如果bean的类修饰符不是public则报错
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
//查看RootBeanDefinition的factor-method属性是不是空的,不为空,说明bean
// 的实现要通过先实例化对应的factoryBean然后调用factoryMethod方法实现,或者直接调用静态的factoryMethod方法
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
//重新创建同一个bean时相关的判断条件
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
//如果缓存的已解析的构造函数或工厂方法对象不为空,则说明这是重新创建同一个bean
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
//如果是重新创建,就直接创建
if (resolved) {
//如果构造函数参数标记是已解析,就直接进行构造,否则重新解析然后创建
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
//使用给出的构造器来创建bean并封装到BeanWrapperImpl中,这个方法在autowireConstructor也有用到
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Need to determine the constructor...
//如果不是重新创建的bean,需要确定要用于给定bean的候选构造函数,检查所有已注册的构造函数
//bean 的生命周期之一,如果实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,会在这里调用determineCandidateConstructors方法
// 这里其实是调用了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors方法
// 然后进行autowireConstructor
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
// 真正处理循环依赖的方法,详见下文
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
//没有特殊处理:只需使用no-arg构造函数
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
public BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(
final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, Constructor<?>[] chosenCtors, final Object[] explicitArgs) {
//先实例化一个BeanWrapperImpl类对象
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
//这里的beanFactory是初始化ConstructorResolver构造器的时候在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的autowireConstructor方法中传进来的就是AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
Constructor<?> constructorToUse = null;
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;
//如果构造参数不为空就直接使用
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
else {
Object[] argsToResolve = null;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
//获取已缓存解析的构造函数或工厂方法(resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod----用于缓存已解析的构造函数或工厂方法)
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
//如果缓存不为空,并且构造参数已经解析缓存了,(constructorArgumentsResolved为包可见,用于表示构造参数状态是否已经解析)
if (constructorToUse != null && mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved) {
// Found a cached constructor...
//获取缓存的构造函数(resolvedConstructorArguments---用于缓存完全解析的构造函数参数的包可见字段)
argsToUse = mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments;
if (argsToUse == null) {
//如果获取到的缓存的构造参数是空,就获取缓存的部分准备的构造函数参数(preparedConstructorArguments---用于缓存部分准备的构造函数参数的包可见字段)
argsToResolve = mbd.preparedConstructorArguments;
}
}
}
//如果缓存的参数不是空,就进行解析,解析时会对argsToResolve中的每个的类型进行转化,也是一个复杂的逻辑
if (argsToResolve != null) {
argsToUse = resolvePreparedArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, constructorToUse, argsToResolve);
}
}
//如果缓存的构造器不存在,就说明没有bean进行过解析,需要去关联对应的bean的构造器
if (constructorToUse == null) {
// Need to resolve the constructor.
//如果传入的构造器不是空的,那么就获取bean的注入模式,如果是空就按照构造器注入方式注入
boolean autowiring = (chosenCtors != null ||
//getResolvedAutowireMode方法逻辑是,如果是自适应注入方法就看有没有无参构造器,如果存在就按照type类型注入,如果不存在就按照构造器方式注入,如果没有设置注入方式就不注入
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
ConstructorArgumentValues resolvedValues = null;
int minNrOfArgs;
//传入的构造参数不为空,这种构造器最小参数个数个传入的个数
if (explicitArgs != null) {
minNrOfArgs = explicitArgs.length;
}
else {
//如果传的构造参数是空的,则从RootBeanDefinition中获取构造器参数,并解析对应的构造参数然后添加到ConstructorArgumentValues中
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
resolvedValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
minNrOfArgs = resolveConstructorArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, cargs, resolvedValues);
}
// Take specified constructors, if any.
Constructor<?>[] candidates = chosenCtors;
//如果传入的构造器为空,则获取bean的Class对象,然后根据bean是不是public修饰的来按照不同的方式获取所有的构造器
if (candidates == null) {
Class<?> beanClass = mbd.getBeanClass();
try {
//getDeclaredConstructors返回所有的构造器(包括public和private修饰的),getConstructors返回public修饰的
candidates = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ?
beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors() : beanClass.getConstructors());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
}
//按照访问方式和数量对构造器进行排序;public>protect>private,在同为public时构造器多的排在前面
AutowireUtils.sortConstructors(candidates);
int minTypeDiffWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Set<Constructor<?>> ambiguousConstructors = null;
List<Exception> causes = null;
//便利排序后的构造器
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
Constructor<?> candidate = candidates[i];
Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
//按照参数个数和构造器的参数类型个数进行比较,如果相等就用这个构造器
if (constructorToUse != null && argsToUse.length > paramTypes.length) {
// Already found greedy constructor that can be satisfied ->
// do not look any further, there are only less greedy constructors left.
break;
}
if (paramTypes.length < minNrOfArgs) {
continue;
}
ArgumentsHolder argsHolder;
//没有找到合适的构造器就进行下面的步骤
//如果ConstructorArgumentValues不为空就说明有构造参数
if (resolvedValues != null) {
try {
String[] paramNames = null;
//检查给定的“java.beans.ConstructorProperties”类型的参数能否被加载,“java.beans.ConstructorProperties”是ConstructorResolver的一个静态常量,是一个Java标签的路径
if (constructorPropertiesAnnotationAvailable) {
//获取有ConstructorProperties标签的参数,因为上面有判断是否可以被加载,所这里直接能够拿到贴了标签的构造参数名称
//ConstructorProperties标签的作用=======》构造函数上的注释,显示该构造函数的参数如何与构造对象的getter方法相对应
paramNames = ConstructorPropertiesChecker.evaluate(candidate, paramTypes.length);
}
//如果paramNames是空,则说明参数没有被获取到,则在beanFactory中获取用于获取方法参数的ParameterNameDiscoverer对象,然后获取参数名称
if (paramNames == null) {
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer();
if (pnd != null) {
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
}
//根据获取到的参数名和已经查到的构造参数和构造参数类型来创建用户创建构造器用的构造参数数组,这个数组中包含了原始的参数列表和构造后的参数列表,用来对比用
//划重点,这里会调用resolveAutowiredArgument方法
//进而调用DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency方法
//进而调用doResolveDependency方法
//进而调用DependencyDescriptor#resolveCandidate方法
//进而调用getBean-->doGetBean来完成一个循环调用的链
//以保证最顶层的bean实例化之前,他所有依赖链上的bean都已经实例化完毕
//此处极为复杂!!
argsHolder = createArgumentArray(
beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw, paramTypes, paramNames, candidate, autowiring);
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
if (this.beanFactory.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.beanFactory.logger.trace(
"Ignoring constructor [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex);
}
if (i == candidates.length - 1 && constructorToUse == null) {
if (causes != null) {
for (Exception cause : causes) {
this.beanFactory.onSuppressedException(cause);
}
}
throw ex;
}
else {
// Swallow and try next constructor.
if (causes == null) {
causes = new LinkedList<Exception>();
}
causes.add(ex);
continue;
}
}
}
else {
// Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly.
if (paramTypes.length != explicitArgs.length) {
continue;
}
argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs);
}
//如果是宽松的构造策略,则对比spring构造的参数数组的类型和获取到的构造器参数的参数类型进行对比,返回不同的个数
//如果是严格的构造策略,则检查能否将构造的参数数组赋值到构造器参数的参数列表中
int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ?
argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes));
// Choose this constructor if it represents the closest match.
if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) {
constructorToUse = candidate;
argsHolderToUse = argsHolder;
argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments;
minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight;
ambiguousConstructors = null;
}
else if (constructorToUse != null && typeDiffWeight == minTypeDiffWeight) {
if (ambiguousConstructors == null) {
ambiguousConstructors = new LinkedHashSet<Constructor<?>>();
ambiguousConstructors.add(constructorToUse);
}
ambiguousConstructors.add(candidate);
}
}
if (constructorToUse == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve matching constructor " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities)");
}
else if (ambiguousConstructors != null && !mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Ambiguous constructor matches found in bean '" + beanName + "' " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities): " +
ambiguousConstructors);
}
if (explicitArgs == null) {
argsHolderToUse.storeCache(mbd, constructorToUse);
}
}
try {
Object beanInstance;
//下面步骤都是一样的,用上面得到的构造器(无论是从bean对象中获取的还是spring自己构建的)和参数来反射创建bean实例,并放到BeanWrapperImpl对象中然后返回
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
final Constructor<?> ctorToUse = constructorToUse;
final Object[] argumentsToUse = argsToUse;
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
return beanFactory.getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(
mbd, beanName, beanFactory, ctorToUse, argumentsToUse);
}
}, beanFactory.getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = this.beanFactory.getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(
mbd, beanName, this.beanFactory, constructorToUse, argsToUse);
}
bw.setWrappedInstance(beanInstance);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
//bean不为空,并且RootBeanDefinition是程序自己定义的,并且实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(一个bean实例化过程中调用的类)
if (bean != null && !mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//获取早期访问指定bean的引用,通常用于解析循环引用。
exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
if (exposedObject == null) {
return null;
}
}
}
}
return exposedObject;
}
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
//获取RootBeanDefinition中bean的属性值
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
//如果BeanWrapper为null说明bean没有实例化成功,会报错
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, to support styles of field injection.
//为任何实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors接口的方法,提供在设置属性之前修改bean状态的机会,就是实例化bean的时候(不是复赋值的时候)
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//调用实现的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
//深拷贝RootBeanDefinition的所有的属性值。保证PropertyValue引用是独立的,但它不能深度复制当前由各个PropertyValue对象引用的对象。
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
//按照按名称注入的方式注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
//按照按名称类型的方式注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
//如果bean实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口或者bean需要进行依赖检查,需要进行处理
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
//一次调用实现的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessPropertyValues方法
//这里会调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues方法
//然后调用InjectionMetadata#inject方法
//进而调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement#inject方法
//进而调用DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency方法
//进而调用doResolveDependency方法
//进而调用DependencyDescriptor#resolveCandidate方法
//进而调用getBean-->doGetBean来完成一个循环调用的链
//以保证最顶层的bean的feild加载之前,他所有依赖链上的feild都已经实例化完毕
//此处极为复杂!!
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
//进行依赖检查,主要检查设置到bean中的数据类型和对象是否个bean对象自身定义的数据类型和对象是不是一样
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
//其中的autowireByName方法解析
protected void autowireByName(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
//获取所有的不是普通属性(普通指的基本类型,字符串,数字类型,日期,URL,URI一个Local类或者一个Class对象)的元素的name(name从BeanWrapper中获取)数组
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
//按照获取的名称去找对应的bean,并添加到依赖缓存集合中记录
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
if (containsBean(propertyName)) {
Object bean = getBean(propertyName);
pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
registerDependentBean(propertyName, beanName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Added autowiring by name from bean name '" + beanName +
"' via property '" + propertyName + "' to bean named '" + propertyName + "'");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Not autowiring property '" + propertyName + "' of bean '" + beanName +
"' by name: no matching bean found");
}
}
}
}
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//如果bean是BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware或者BeanFactoryAware其中某一个的实现类就需要进行处理
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
//bean的生命周期之一。如果实现了BeanPostProcessor接口则在这里调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
//bean的生命周期之一,如果实现了InitializingBean接口,会在这里调用实现的afterPropertiesSet方法
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
//bean的生命周期之一。如果实现了BeanPostProcessor接口则在这里调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
bean都加载完了,最最后finishRefresh
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
// 1.为此上下文初始化生命周期处理器
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
// 2.首先将刷新完毕事件传播到生命周期处理器(触发isAutoStartup方法返回true的SmartLifecycle的start方法)
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
// 3.推送上下文刷新完毕事件到相应的监听器
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
关于循环依赖
最后说一下spring如何解决property上的循环依赖
Spring容器的’三级缓存’
在Spring容器的整个声明周期中,单例Bean有且仅有一个对象。这很容易让人想到可以用缓存来加速访问。
从源码中也可以看出Spring大量运用了Cache的手段,在循环依赖问题的解决过程中甚至不惜使用了“三级缓存”,这也便是它设计的精妙之处~
三级缓存其实它更像是Spring容器工厂的内的术语,采用三级缓存模式来解决循环依赖问题,这三级缓存分别指:
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
...
// 从上至下 分表代表这“三级缓存”
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256); //一级缓存
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16); // 二级缓存
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16); // 三级缓存
...
/** Names of beans that are currently in creation. */
// 这个缓存也十分重要:它表示bean创建过程中都会在里面呆着~
// 它在Bean开始创建时放值,创建完成时会将其移出~
private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
/** Names of beans that have already been created at least once. */
// 当这个Bean被创建完成后,会标记为这个 注意:这里是set集合 不会重复
// 至少被创建了一次的 都会放进这里~~~~
private final Set<String> alreadyCreated = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256));
}
注:AbstractBeanFactory继承自DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry~
- singletonObjects:用于存放完全初始化好的 bean,从该缓存中取出的 bean 可以直接使用
- earlySingletonObjects:提前曝光的单例对象的cache,存放原始的 bean 对象(尚未填充属性),用于解决循环依赖
- singletonFactories:单例对象工厂的cache,存放 bean 工厂对象,用于解决循环依赖
加载过程上文分析过,这里重新总结下:
- 先从一级缓存singletonObjects中去获取。(如果获取到就直接return)
- 如果获取不到或者对象正在创建中(isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation()),那就再从二级缓存earlySingletonObjects中获取。(如果获取到就直接return)
- 如果还是获取不到,且允许singletonFactories(allowEarlyReference=true)通过getObject()获取。就从三级缓存singletonFactory.getObject()获取。(如果获取到了就从singletonFactories中移除,并且放进earlySingletonObjects。其实也就是从三级缓存移动(是剪切、不是复制哦~)到了二级缓存)
所以才有了这段代码
protected Object doCreateBean( ... ){
...
// 这段告诉我们:如果允许循环依赖的话,此处会添加一个ObjectFactory到三级缓存里面,以备创建对象并且提前暴露引用~
// 此处Tips:getEarlyBeanReference是后置处理器SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的一个方法,它的功效为:
// 保证自己被循环依赖的时候,即使被别的Bean @Autowire进去的也是代理对象~~~~ AOP自动代理创建器此方法里会创建的代理对象~~~
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) { // 需要提前暴露(支持循环依赖),就注册一个ObjectFactory到三级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// 此处注意:如果此处自己被循环依赖了 那它会走上面的getEarlyBeanReference,从而创建一个代理对象从三级缓存转移到二级缓存里
// 注意此时候对象还在二级缓存里,并没有在一级缓存。并且此时可以知道exposedObject仍旧是原始对象~~~
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
// 经过这两大步后,exposedObject还是原始对象(注意此处以事务的AOP为例子的,
// 因为事务的AOP自动代理创建器在getEarlyBeanReference创建代理后,initializeBean就不会再重复创建了,二选一的,下面会有描述~~~)
...
// 循环依赖校验(非常重要)~~~~
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// 前面说了因为自己被循环依赖了,所以此时候代理对象还在二级缓存里~~~(备注:本利讲解的是自己被循环依赖了的情况)
// so,此处getSingleton,就会把里面的对象拿出来,我们知道此时候它已经是个Proxy代理对象~~~
// 最后赋值给exposedObject 然后return出去,进而最终被addSingleton()添加进一级缓存里面去
// 这样就保证了我们容器里**最终实际上是代理对象**,而非原始对象~~~~~
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) { // 这个判断不可少(因为如果initializeBean改变了exposedObject ,就不能这么玩了,否则就是两个对象了~~~)
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
}
...
}
}
其实就是为了解决循环依赖,spring会提前把实例加载到三级缓存中去,然后依赖链上的实例创建后,如果需要这个之前缓存的实例,就会先在二级缓存中找,找不到再去三级缓存里找,找到了再把它移出三级缓存,拿到二级缓存里,并用它来装配对象的属性,最后都搞定后,再把二级缓存中的实例拿到一级缓存里去保存。
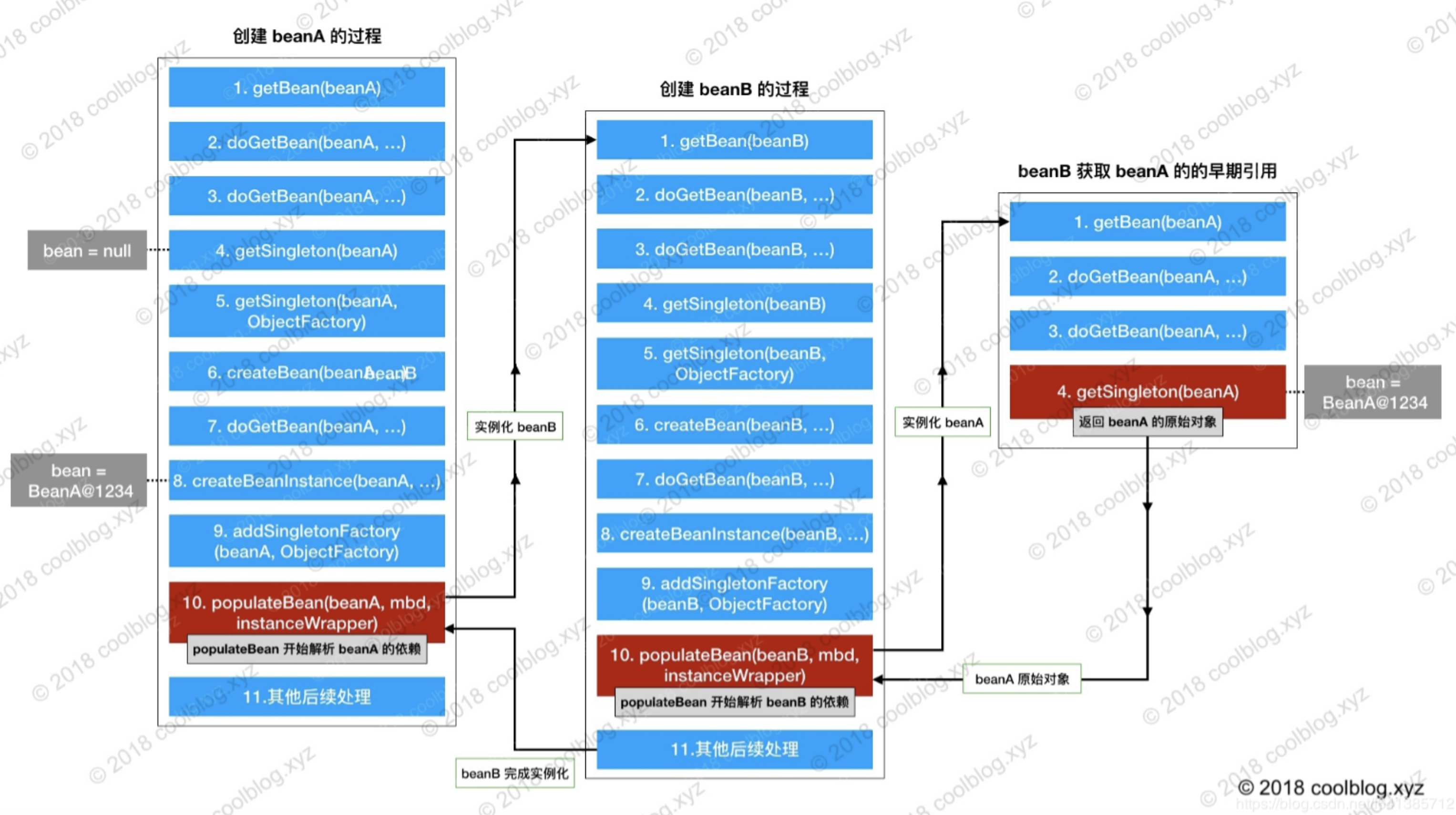
最后说一下,为什么构造器循环依赖不行
其实前文源码阅读已经说过了,bean的实例化也是依赖构造器的,在检查到构造器有依赖时,会把这个构造器的依赖链上的所有依赖的bean,都通过构造器实例化一遍,这样A发现自己的构造器依赖B,就去实例化B,B也发现自己的构造器依赖A,也去实例化A,而这时候,A已经开始实例化了(spring里有一个cache标志了正在实例化的实例),这样就会产生冲突而报错。
field(property)注入因为已经通过无参构造器完成了实例化,然后在注入property,所以不存在问题。
关于解决依赖
上文已经提过,实际上依赖的解决是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor做的,他调用的是resolveDependency
关于自动装配
上文已经提过,实际上是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor做的,他会处理所有@import的类,进而去找SpringFactoriesLoader里的东西进行bean definition的注册
不得不说,spring确实太复杂了,搞了两天才搞完。