设计模式
http://c.biancheng.net/view/8385.html 这篇文章对Java设计模式有十分全面的介绍。本文结合网上资料和自己经验总结一些设计模式的案例。
单例模式
简单的
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null)
instance = new Singleton();
return instance;
}
双重检查
为什么要双重检查
如果不加内层检查,两个线程可以同时进入if创建实例
如果不加外层检查,会重复上锁影响性能
// 注意一定要用volatile来避免指令重排
private volatile static Singleton instance;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null)
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
return instance;
}
静态内部类
class Singleton {
public static Singleton instance;
private static class SingletonWrapper {
static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
}
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return SingletonWrapper.instance;
}
}
枚举
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton.INSTANCE.sayHello();
}
}
enum Singleton {
INSTANCE;
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
工厂模式
简单工厂
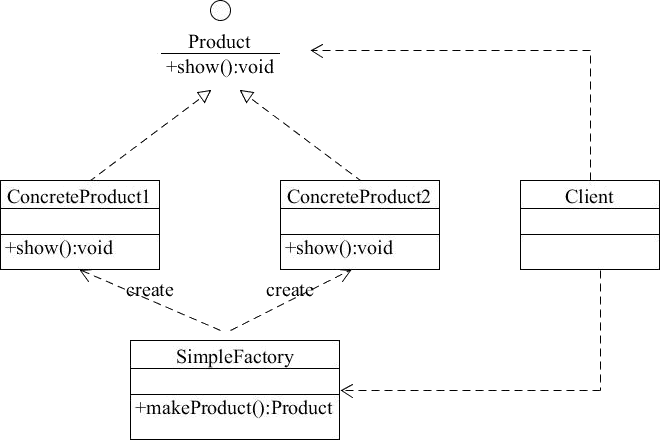
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//抽象产品
public interface Product {
void show();
}
//具体产品:ProductA
static class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
public void show() {
System.out.println("具体产品1显示...");
}
}
//具体产品:ProductB
static class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
public void show() {
System.out.println("具体产品2显示...");
}
}
final class Const {
static final int PRODUCT_A = 0;
static final int PRODUCT_B = 1;
static final int PRODUCT_C = 2;
}
static class SimpleFactory {
public static Product makeProduct(int kind) {
switch (kind) {
case Const.PRODUCT_A:
return new ConcreteProduct1();
case Const.PRODUCT_B:
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
return null;
}
}
}
简单工厂模式没啥好说的,因为它太简单了。代码直接略过。唯一要说的是提供一种spring下的工厂模式实现思路,可以把一个接口的所有实现类都注册成bean,然后通过不同bean的名字来实现一个简单工厂,我在做分布式锁的时候用过这种方式,代码更简洁优雅。详见这里
工厂方法
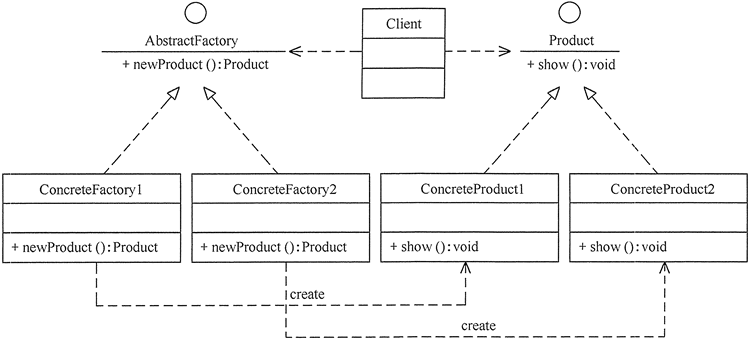
package FactoryMethod;
public class AbstractFactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Product a;
AbstractFactory af;
af = (AbstractFactory) ReadXML1.getObject();
a = af.newProduct();
a.show();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//抽象产品:提供了产品的接口
interface Product {
public void show();
}
//具体产品1:实现抽象产品中的抽象方法
class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
public void show() {
System.out.println("具体产品1显示...");
}
}
//具体产品2:实现抽象产品中的抽象方法
class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
public void show() {
System.out.println("具体产品2显示...");
}
}
//抽象工厂:提供了厂品的生成方法
interface AbstractFactory {
public Product newProduct();
}
//具体工厂1:实现了厂品的生成方法
class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory {
public Product newProduct() {
System.out.println("具体工厂1生成-->具体产品1...");
return new ConcreteProduct1();
}
}
//具体工厂2:实现了厂品的生成方法
class ConcreteFactory2 implements AbstractFactory {
public Product newProduct() {
System.out.println("具体工厂2生成-->具体产品2...");
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
}
抽象工厂
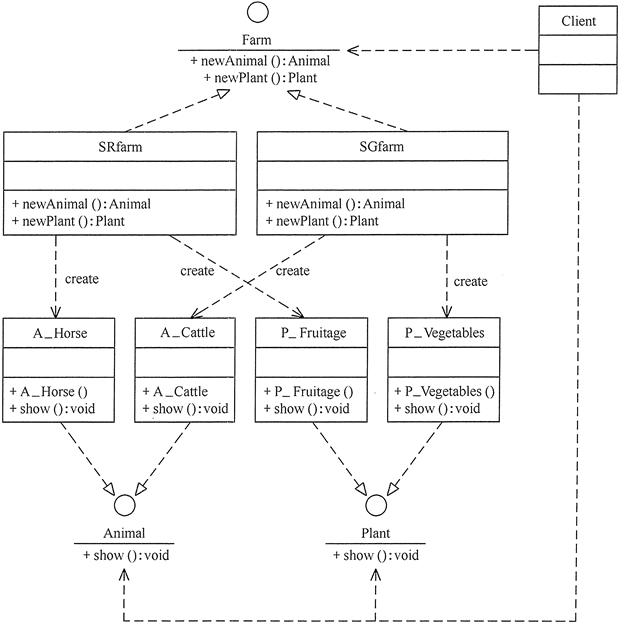
package AbstractFactory;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FarmTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Farm f;
Animal a;
Plant p;
f = (Farm) ReadXML.getObject();
a = f.newAnimal();
p = f.newPlant();
a.show();
p.show();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//抽象产品:动物类
interface Animal {
public void show();
}
//具体产品:马类
class Horse implements Animal {
JScrollPane sp;
JFrame jf = new JFrame("抽象工厂模式测试");
public Horse() {
Container contentPane = jf.getContentPane();
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 1));
p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("动物:马"));
sp = new JScrollPane(p1);
contentPane.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JLabel l1 = new JLabel(new ImageIcon("src/A_Horse.jpg"));
p1.add(l1);
jf.pack();
jf.setVisible(false);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//用户点击窗口关闭
}
public void show() {
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
//具体产品:牛类
class Cattle implements Animal {
JScrollPane sp;
JFrame jf = new JFrame("抽象工厂模式测试");
public Cattle() {
Container contentPane = jf.getContentPane();
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 1));
p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("动物:牛"));
sp = new JScrollPane(p1);
contentPane.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JLabel l1 = new JLabel(new ImageIcon("src/A_Cattle.jpg"));
p1.add(l1);
jf.pack();
jf.setVisible(false);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//用户点击窗口关闭
}
public void show() {
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
//抽象产品:植物类
interface Plant {
public void show();
}
//具体产品:水果类
class Fruitage implements Plant {
JScrollPane sp;
JFrame jf = new JFrame("抽象工厂模式测试");
public Fruitage() {
Container contentPane = jf.getContentPane();
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 1));
p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("植物:水果"));
sp = new JScrollPane(p1);
contentPane.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JLabel l1 = new JLabel(new ImageIcon("src/P_Fruitage.jpg"));
p1.add(l1);
jf.pack();
jf.setVisible(false);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//用户点击窗口关闭
}
public void show() {
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
//具体产品:蔬菜类
class Vegetables implements Plant {
JScrollPane sp;
JFrame jf = new JFrame("抽象工厂模式测试");
public Vegetables() {
Container contentPane = jf.getContentPane();
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 1));
p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("植物:蔬菜"));
sp = new JScrollPane(p1);
contentPane.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JLabel l1 = new JLabel(new ImageIcon("src/P_Vegetables.jpg"));
p1.add(l1);
jf.pack();
jf.setVisible(false);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//用户点击窗口关闭
}
public void show() {
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
//抽象工厂:农场类
interface Farm {
public Animal newAnimal();
public Plant newPlant();
}
//具体工厂:韶关农场类
class SGfarm implements Farm {
public Animal newAnimal() {
System.out.println("新牛出生!");
return new Cattle();
}
public Plant newPlant() {
System.out.println("蔬菜长成!");
return new Vegetables();
}
}
//具体工厂:上饶农场类
class SRfarm implements Farm {
public Animal newAnimal() {
System.out.println("新马出生!");
return new Horse();
}
public Plant newPlant() {
System.out.println("水果长成!");
return new Fruitage();
}
}
建造者模式(Bulider模式)
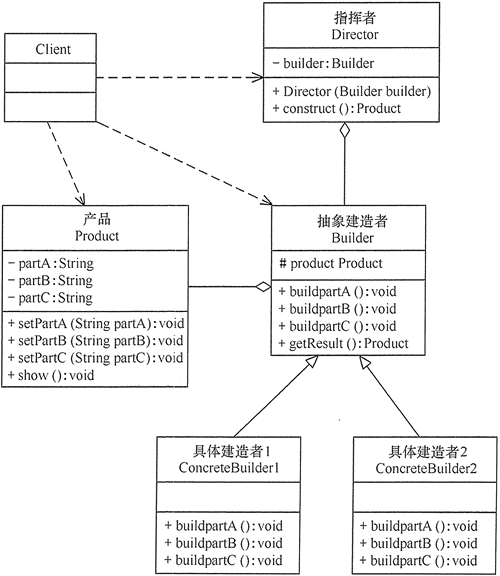
class Product
{
private String partA;
private String partB;
private String partC;
public void setPartA(String partA)
{
this.partA=partA;
}
public void setPartB(String partB)
{
this.partB=partB;
}
public void setPartC(String partC)
{
this.partC=partC;
}
public void show()
{
//显示产品的特性
}
}
abstract class Builder
{
//创建产品对象
protected Product product=new Product();
public abstract void buildPartA();
public abstract void buildPartB();
public abstract void buildPartC();
//返回产品对象
public Product getResult()
{
return product;
}
}
public class ConcreteBuilder extends Builder
{
public void buildPartA()
{
product.setPartA("建造 PartA");
}
public void buildPartB()
{
product.setPartB("建造 PartB");
}
public void buildPartC()
{
product.setPartC("建造 PartC");
}
}
class Director
{
private Builder builder;
public Director(Builder builder)
{
this.builder=builder;
}
//产品构建与组装方法
public Product construct()
{
builder.buildPartA();
builder.buildPartB();
builder.buildPartC();
return builder.getResult();
}
}
public class Client
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Builder builder=new ConcreteBuilder();
Director director=new Director(builder);
Product product=director.construct();
product.show();
}
}
代理模式
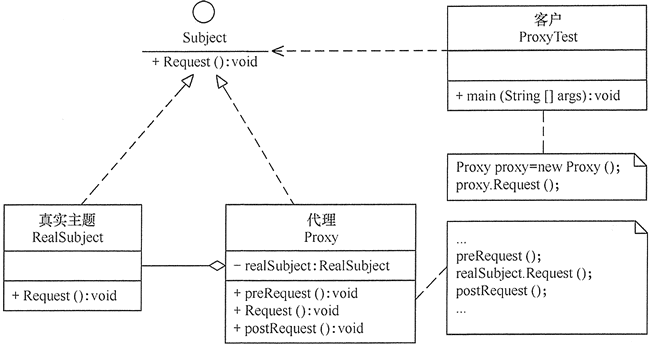
package proxy;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Proxy proxy = new Proxy();
proxy.Request();
}
}
//抽象主题
interface Subject {
void Request();
}
//真实主题
class RealSubject implements Subject {
public void Request() {
System.out.println("访问真实主题方法...");
}
}
//代理
class Proxy implements Subject {
private RealSubject realSubject;
public void Request() {
if (realSubject == null) {
realSubject = new RealSubject();
}
preRequest();
realSubject.Request();
postRequest();
}
public void preRequest() {
System.out.println("访问真实主题之前的预处理。");
}
public void postRequest() {
System.out.println("访问真实主题之后的后续处理。");
}
}
适配器模式(Adapter模式)
类适配器模式
接口实现类调用另一个子类的方法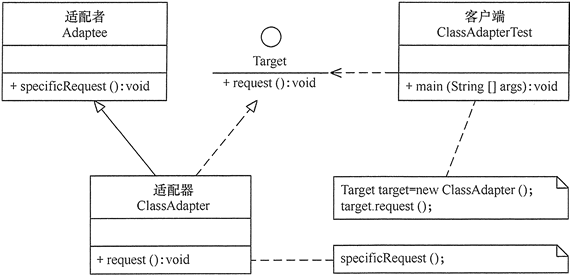
package adapter;
//目标接口
interface Target
{
public void request();
}
//适配者接口
class Adaptee
{
public void specificRequest()
{
System.out.println("适配者中的业务代码被调用!");
}
}
//类适配器类
class ClassAdapter extends Adaptee implements Target
{
public void request()
{
specificRequest();
}
}
//客户端代码
public class ClassAdapterTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("类适配器模式测试:");
Target target = new ClassAdapter();
target.request();
}
}
对象适配器模式
用适配对象去实现接口,调用适配器方法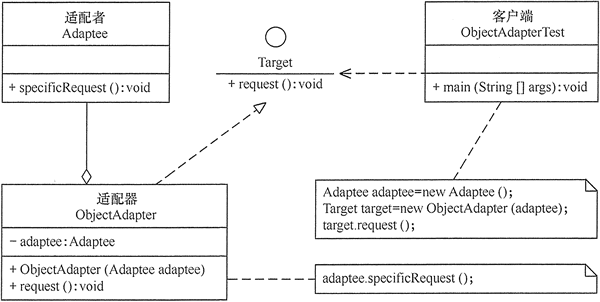
package adapter;
//对象适配器类
class ObjectAdapter implements Target
{
private Adaptee adaptee;
public ObjectAdapter(Adaptee adaptee)
{
this.adaptee=adaptee;
}
public void request()
{
adaptee.specificRequest();
}
}
//客户端代码
public class ObjectAdapterTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("对象适配器模式测试:");
Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee();
Target target = new ObjectAdapter(adaptee);
target.request();
}
}
桥接模式(Bridge模式)
通过一个抽象类对一个接口的引用实现桥接
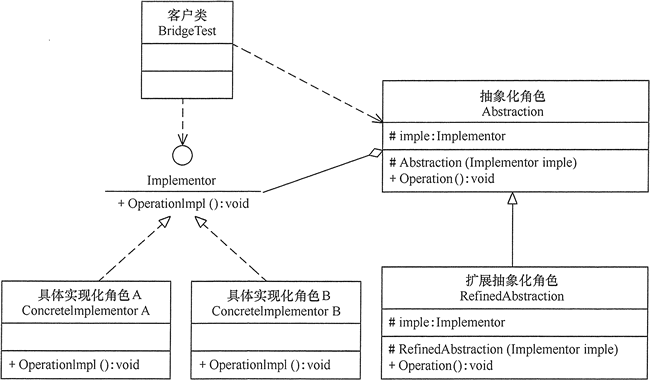
package bridge;
public class BridgeTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Implementor imple=new ConcreteImplementorA();
Abstraction abs=new RefinedAbstraction(imple);
abs.Operation();
}
}
//实现化角色
interface Implementor
{
public void OperationImpl();
}
//具体实现化角色
class ConcreteImplementorA implements Implementor
{
public void OperationImpl()
{
System.out.println("具体实现化(Concrete Implementor)角色被访问" );
}
}
//抽象化角色
abstract class Abstraction
{
protected Implementor imple;
protected Abstraction(Implementor imple)
{
this.imple=imple;
}
public abstract void Operation();
}
//扩展抽象化角色
class RefinedAbstraction extends Abstraction
{
protected RefinedAbstraction(Implementor imple)
{
super(imple);
}
public void Operation()
{
System.out.println("扩展抽象化(Refined Abstraction)角色被访问" );
imple.OperationImpl();
}
}
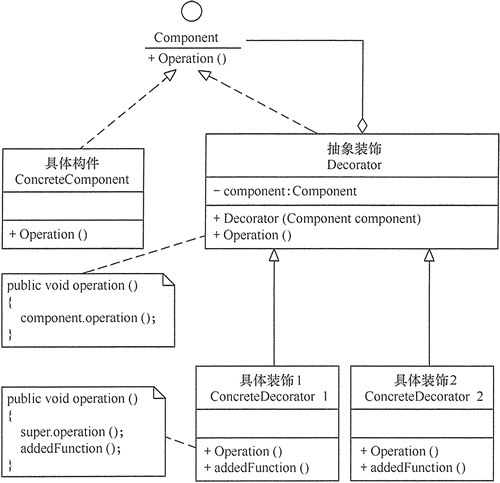
装饰(Decorator)模式
装饰者和具体实现,实现同一个接口,装饰者为借口方法提供额外功能
package decorator;
public class DecoratorPattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Component p=new ConcreteComponent();
p.operation();
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
Component d=new ConcreteDecorator(p);
d.operation();
}
}
//抽象构件角色
interface Component
{
public void operation();
}
//具体构件角色
class ConcreteComponent implements Component
{
public ConcreteComponent()
{
System.out.println("创建具体构件角色");
}
public void operation()
{
System.out.println("调用具体构件角色的方法operation()");
}
}
//抽象装饰角色
class Decorator implements Component
{
private Component component;
public Decorator(Component component)
{
this.component=component;
}
public void operation()
{
component.operation();
}
}
//具体装饰角色
class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator
{
public ConcreteDecorator(Component component)
{
super(component);
}
public void operation()
{
super.operation();
addedFunction();
}
public void addedFunction()
{
System.out.println("为具体构件角色增加额外的功能addedFunction()");
}
}
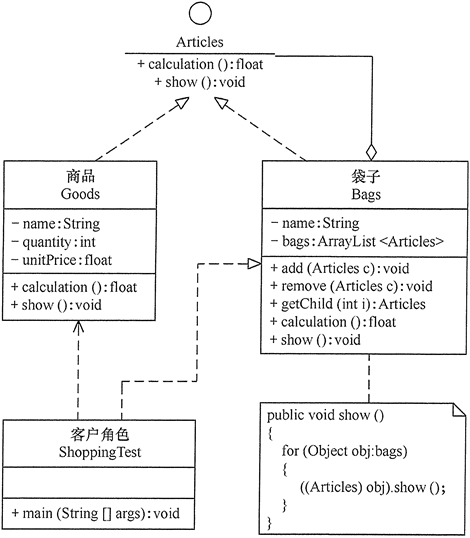
组合模式
package composite;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ShoppingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float s = 0;
Bags BigBag, mediumBag, smallRedBag, smallWhiteBag;
Goods sp;
BigBag = new Bags("大袋子");
mediumBag = new Bags("中袋子");
smallRedBag = new Bags("红色小袋子");
smallWhiteBag = new Bags("白色小袋子");
sp = new Goods("婺源特产", 2, 7.9f);
smallRedBag.add(sp);
sp = new Goods("婺源地图", 1, 9.9f);
smallRedBag.add(sp);
sp = new Goods("韶关香菇", 2, 68);
smallWhiteBag.add(sp);
sp = new Goods("韶关红茶", 3, 180);
smallWhiteBag.add(sp);
sp = new Goods("景德镇瓷器", 1, 380);
mediumBag.add(sp);
mediumBag.add(smallRedBag);
sp = new Goods("李宁牌运动鞋", 1, 198);
BigBag.add(sp);
BigBag.add(smallWhiteBag);
BigBag.add(mediumBag);
System.out.println("您选购的商品有:");
BigBag.show();
s = BigBag.calculation();
System.out.println("要支付的总价是:" + s + "元");
}
}
//抽象构件:物品
interface Articles {
public float calculation(); //计算
public void show();
}
//树叶构件:商品
class Goods implements Articles {
private String name; //名字
private int quantity; //数量
private float unitPrice; //单价
public Goods(String name, int quantity, float unitPrice) {
this.name = name;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
public float calculation() {
return quantity * unitPrice;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(name + "(数量:" + quantity + ",单价:" + unitPrice + "元)");
}
}
//树枝构件:袋子
class Bags implements Articles {
private String name; //名字
private ArrayList<Articles> bags = new ArrayList<Articles>();
public Bags(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void add(Articles c) {
bags.add(c);
}
public void remove(Articles c) {
bags.remove(c);
}
public Articles getChild(int i) {
return bags.get(i);
}
public float calculation() {
float s = 0;
for (Object obj : bags) {
s += ((Articles) obj).calculation();
}
return s;
}
public void show() {
for (Object obj : bags) {
((Articles) obj).show();
}
}
}
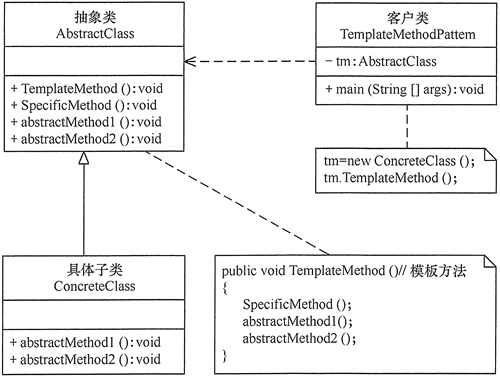
模板方法(Template Method)模式
public class TemplateMethodPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractClass tm = new ConcreteClass();
tm.TemplateMethod();
}
}
//抽象类
abstract class AbstractClass {
//模板方法
public void TemplateMethod() {
SpecificMethod();
abstractMethod1();
abstractMethod2();
}
//具体方法
public void SpecificMethod() {
System.out.println("抽象类中的具体方法被调用...");
}
//抽象方法1
public abstract void abstractMethod1();
//抽象方法2
public abstract void abstractMethod2();
}
//具体子类
class ConcreteClass extends AbstractClass {
public void abstractMethod1() {
System.out.println("抽象方法1的实现被调用...");
}
public void abstractMethod2() {
System.out.println("抽象方法2的实现被调用...");
}
}
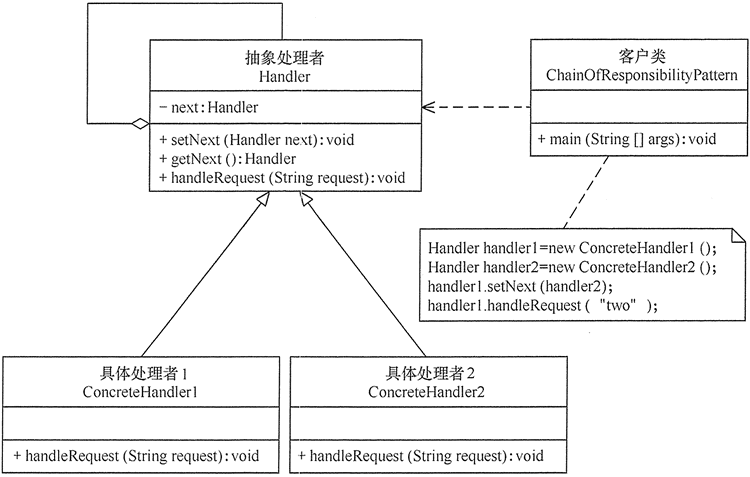
责任链(Chain of Responsibility)模式
package chainOfResponsibility;
public class ChainOfResponsibilityPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//组装责任链
Handler handler1 = new ConcreteHandler1();
Handler handler2 = new ConcreteHandler2();
handler1.setNext(handler2);
//提交请求
handler1.handleRequest("two");
}
}
//抽象处理者角色
abstract class Handler {
private Handler next;
public void setNext(Handler next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Handler getNext() {
return next;
}
//处理请求的方法
public abstract void handleRequest(String request);
}
//具体处理者角色1
class ConcreteHandler1 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("one")) {
System.out.println("具体处理者1负责处理该请求!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("没有人处理该请求!");
}
}
}
}
//具体处理者角色2
class ConcreteHandler2 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("two")) {
System.out.println("具体处理者2负责处理该请求!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("没有人处理该请求!");
}
}
}
}
观察者模式(Observer模式)
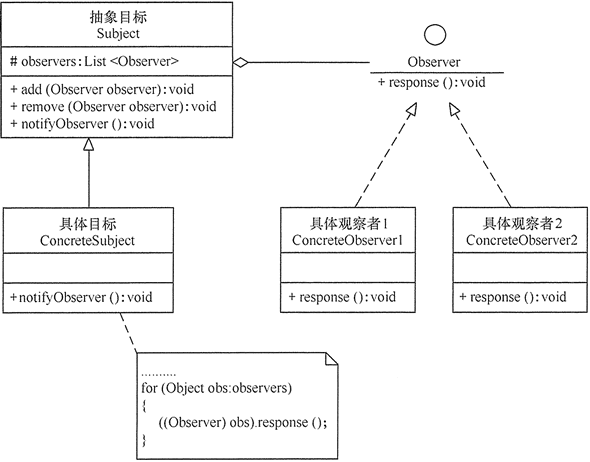
package net.biancheng.c.observer;
import java.util.*;
public class ObserverPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject = new ConcreteSubject();
Observer obs1 = new ConcreteObserver1();
Observer obs2 = new ConcreteObserver2();
subject.add(obs1);
subject.add(obs2);
subject.notifyObserver();
}
}
//抽象目标
abstract class Subject {
protected List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<Observer>();
//增加观察者方法
public void add(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
//删除观察者方法
public void remove(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
}
public abstract void notifyObserver(); //通知观察者方法
}
//具体目标
class ConcreteSubject extends Subject {
public void notifyObserver() {
System.out.println("具体目标发生改变...");
System.out.println("--------------");
for (Object obs : observers) {
((Observer) obs).response();
}
}
}
//抽象观察者
interface Observer {
void response(); //反应
}
//具体观察者1
class ConcreteObserver1 implements Observer {
public void response() {
System.out.println("具体观察者1作出反应!");
}
}
//具体观察者1
class ConcreteObserver2 implements Observer {
public void response() {
System.out.println("具体观察者2作出反应!");
}
}